1.1 Why Graphs
왜 그래프인가?
- 그래프는 상호간의 연관관계를 가진 개체를 분석하고 설명하기 위한 표현이기 때문에 다른 데이터에 비해 연관관계 분석에 장점을 가진다.
그렇다면, 관계형 구조에서 더 나은 예측(prediction)을 하기 위해서는 어떻게 해야 하는가?
- 복잡한 분야(domain)에서는 다채로운(복잡한) 관계형 구조를 가지며, 이것은 relational graph로 표현할 수 있다.
→ explicitly modeling relationship은 더 나은 성능을 확보할 수 있다.
(문제점) 최근의 딥러닝은 텍스트나 이미지와 같이 간단한 시퀀스나 그리드를 위해 설계되었다. 하지만, 모든 데이터가 시퀀스나 그리드로 표현될 수 있는 것이 아니다.
그렇다면, 다양한 영역에서 neural networks를 적용하기 위해서는 어떻게 해야 하는가?
→ Graphs are the new frontier of deep learning.
Graph Deep Learning이 어려운 이유는 네트워크가 복잡하기 때문이다.
- 임의의 크기와 복잡한 위상을 가짐(그리드 처럼 공간적인 균형이 없음)
- 고정된 노드 혹은 참고할 포인트가 없음
- 유동적이고 multimodel features를 가짐
Deep Learning in Graphs
- Input: Networks
- Output(Predictions): Node labels, New links, Generated graphs and subgraphs
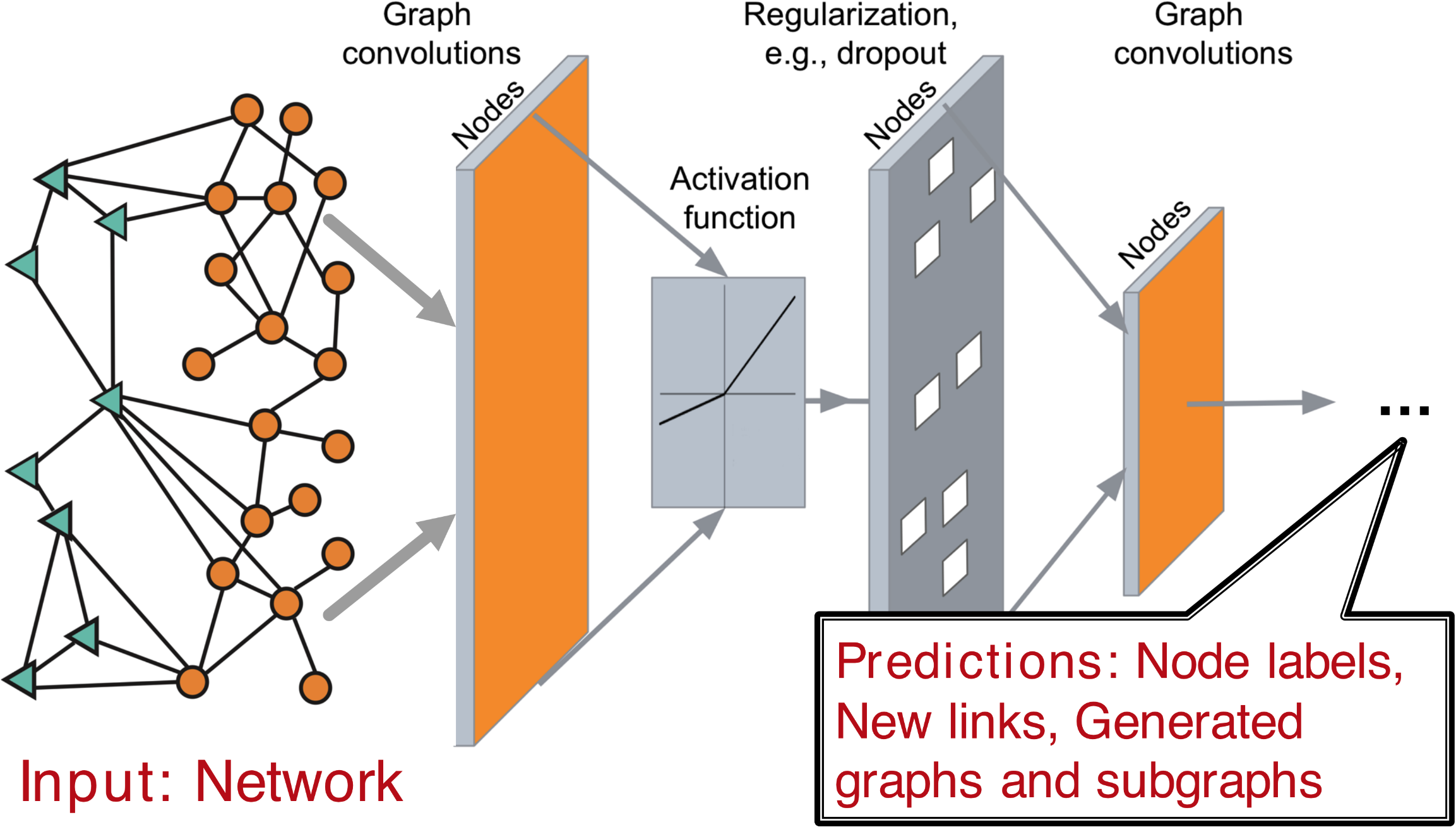
- Raw Data → Graph Data → Learning Algorithms → Model을 거치며, Supervised Machine Learning과 달리, Feature Engineering을 하지 않고, Representation Learning(extract learning features)을 통해 자동으로 feature를 학습하도록 한다.
Representation Learning은 노드를 d-dimensional embeddings space에 사상(map)시킴
→ 그래프 내부의 유사한 노드끼리 가까운 공간에 위치하도록 임베딩
1.2 Applications of Graph ML
Graph ML Tasks
- Node classification: 노드의 속성을 예측 - 온라인 유저/아이템을 카테고리화
- Link prediction: 두 개의 노드 간 missing link가 있는지 없는지 예측 - knowledge graph 완성
- Graph classification: 그래프를 카테고리화 - 분자 속성 예측
- Clustering: 노드가 커뮤니티(community)를 구성하고 있는지 탐지 - social circle 탐지
- Others
- Graph generation: 약물 발견
- Graph evolution: 물리적 시뮬레이션
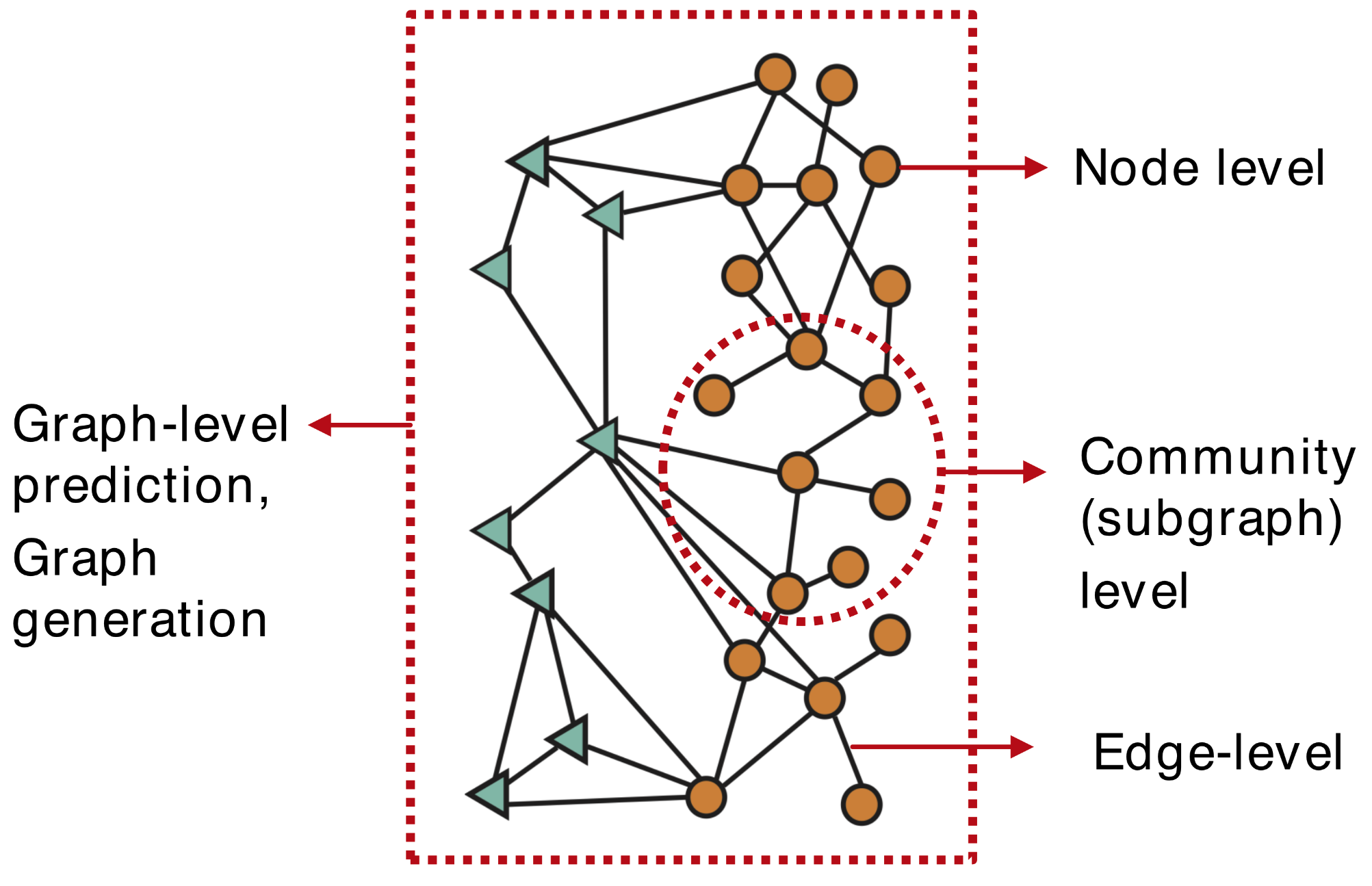
- Node-level ML Tasks
- Protein Folding
- The Protein Folding Problem: 아미노산 스퀀스를 기반으로 단백질의 3D구조를 계산적으로 예측
- AlphaFold
- Key idea: Spatial Graph
- Nodes: 단백질 시퀀스 내 아미노산
- Edges: 아미노산 끼리의 proximity
- Key idea: Spatial Graph
- Protein Folding
- Edge-level ML Tasks
- Recommender Systems
- Goal: 사용자가 좋아할 아이템을 추천
- PinSage: Graph-based Recommender: 그래프 내 두 개의 노드가 서로 연관되어있는지 예측
- Drug Side Effects: 약물 한 쌍이 주어졌을때, 부정적인 side effect를 예측
- Biomedical Graph Link Prediction
- Nodes: 약물과 단백질
- Edges: 상호작용(interactions)
- Biomedical Graph Link Prediction
- Recommender Systems
- Subgraph-level ML Tasks
- Traffic Prediction
- Road Networks as a Graph
- Nodes: Road 세그먼트
- Edges: Road 세그먼트 간 연결성
- Road Networks as a Graph
- Traffic Prediction
- Graph-level ML Tasks
- Drug Discovery
- Antibiotics are small molecular graphs
- Nodes: 원자
- Edges: 화학적 유대(chemical bonds)
- Antibiotics are small molecular graphs
- Graph Generation: Generating novel 분자(molecule)
- Physical Simulation
- Nodes: Particles
- Edges: Particle간 상호작용
- Graph evolution task: 그래프가 어떻게 진화(변화)할 것인지 예측
- Drug Discovery
1.3 Choice of Graph Representation
네트워크의 구성요소
- Objects: nodes, vertices $N$
- Interactions: links, edges $E$
- System: network, graphs $G(N,E)$
그래프를 정의하는 방법
- 주어진 문제(problem)과 분야(domain)에서, 적합한 network representation을 선택하는 것이 성공적으로 활용할 수 있도록 만들어 줌
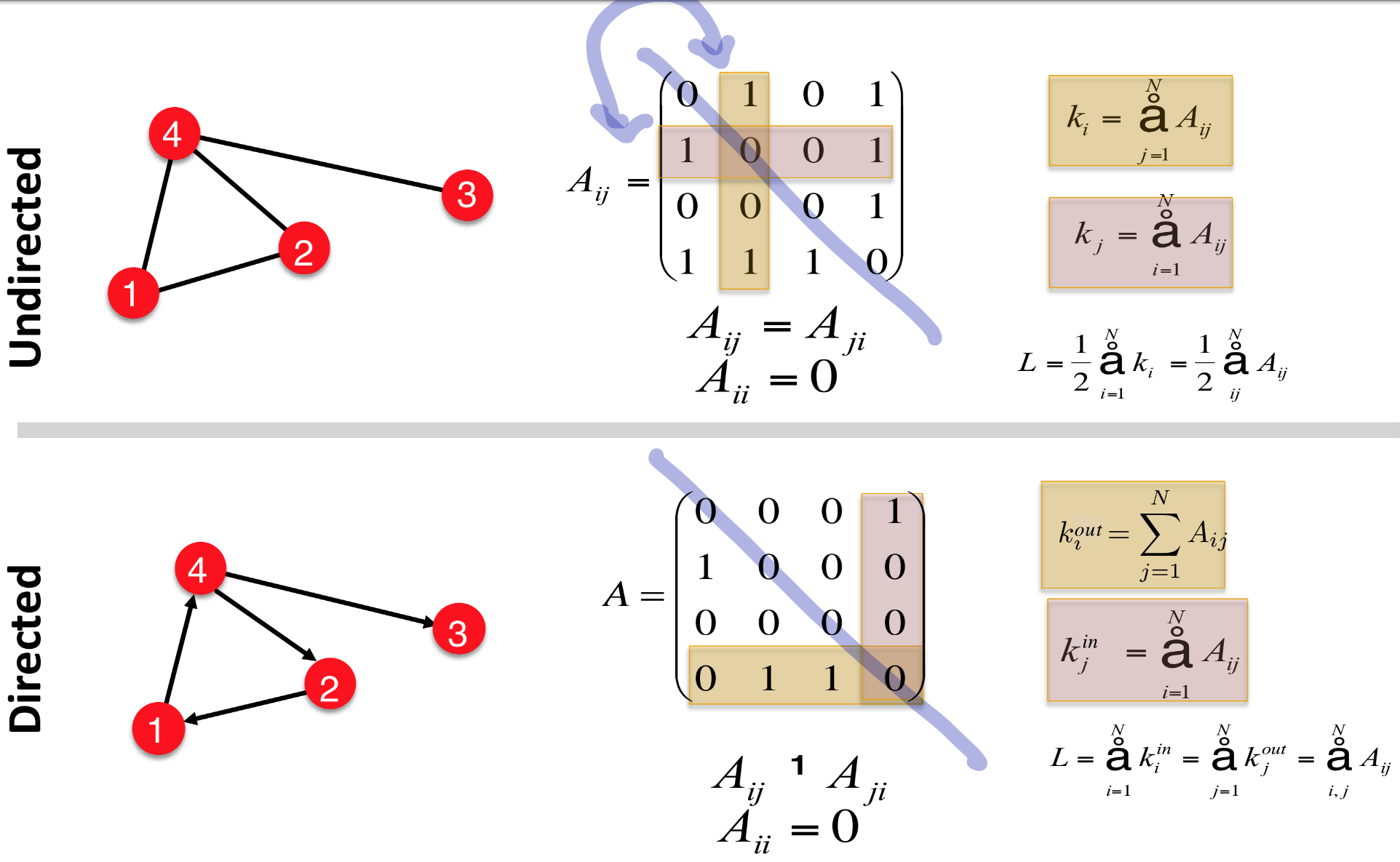
Directed vs. Undirected Graphs
- Undirected: undirected links - 협력관계, 페이스북 친구
- Directed: directed links - 전화통화, 트위터 팔로우
Heterogeneous Graphs
- a heterogeneous graph is defined as $G = (V,E,R,T)$
- Nodes with node types $v_i \in V$
- Edges with relation types $(v_i,r,v_j) \in E$
- Node type $T(v_i)$
- Relation type $r \in R$
Node degree, $k_i$: 노드 i에 인접한 엣지의 수
- 평균 degree: $\overline{k}=\lang k \rang=\frac{1}{N}\mathring{a}_{i=1}^Nk_i=\frac{2E}{N}$
- directed graph에서는 in-degree와 out-degree로 나눌 수 있음
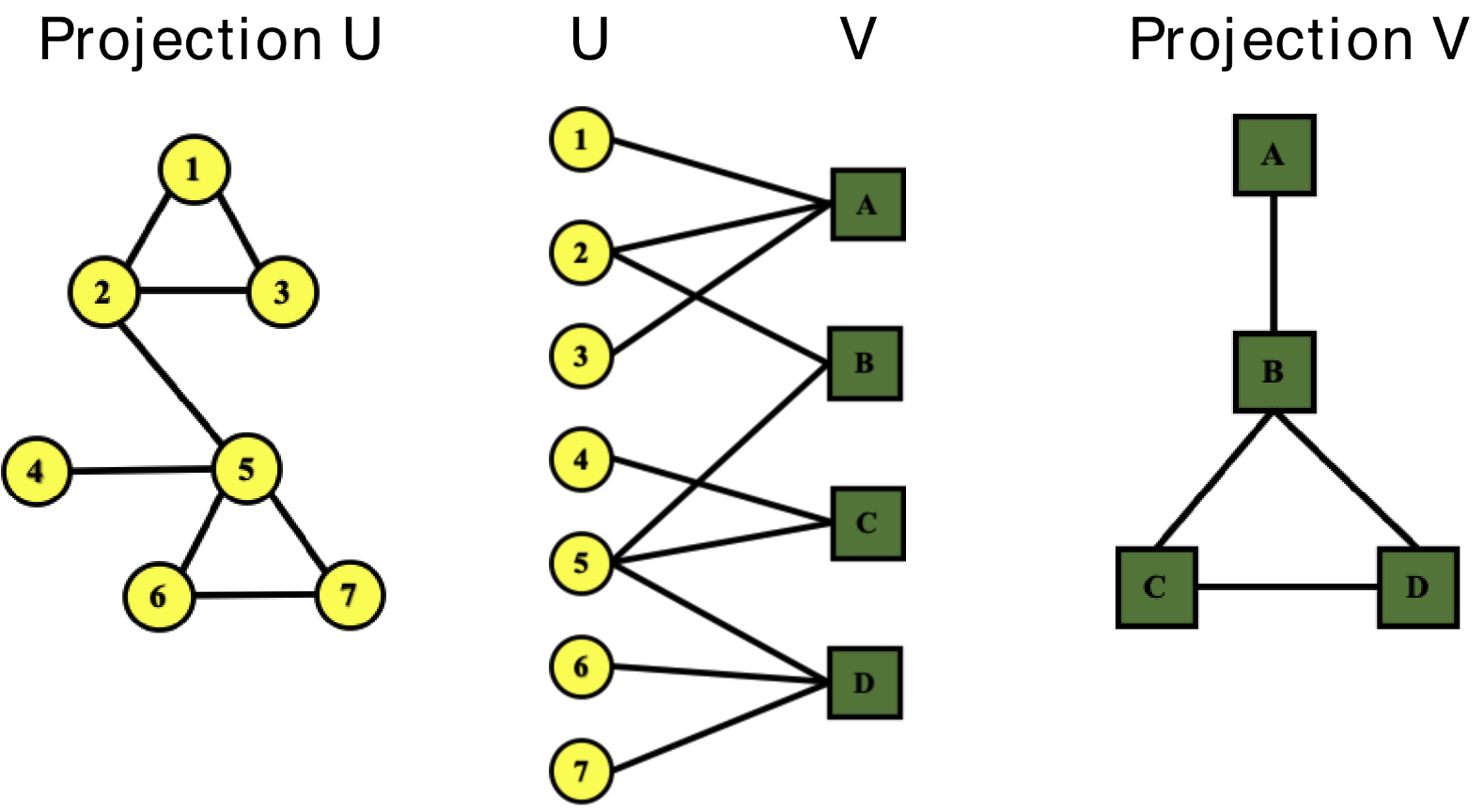
Bipartite Graph: 서로 연결관계가 없는 집합 $U$와 집합 $V$로 나뉜 그래프
Folded/Projected Bipartite Graph
- Bipartite Graph를 프로젝션 시켜서, 그래프를 생성할 수 있음
Representing Graphs
Adjacency Matrix
Edge list
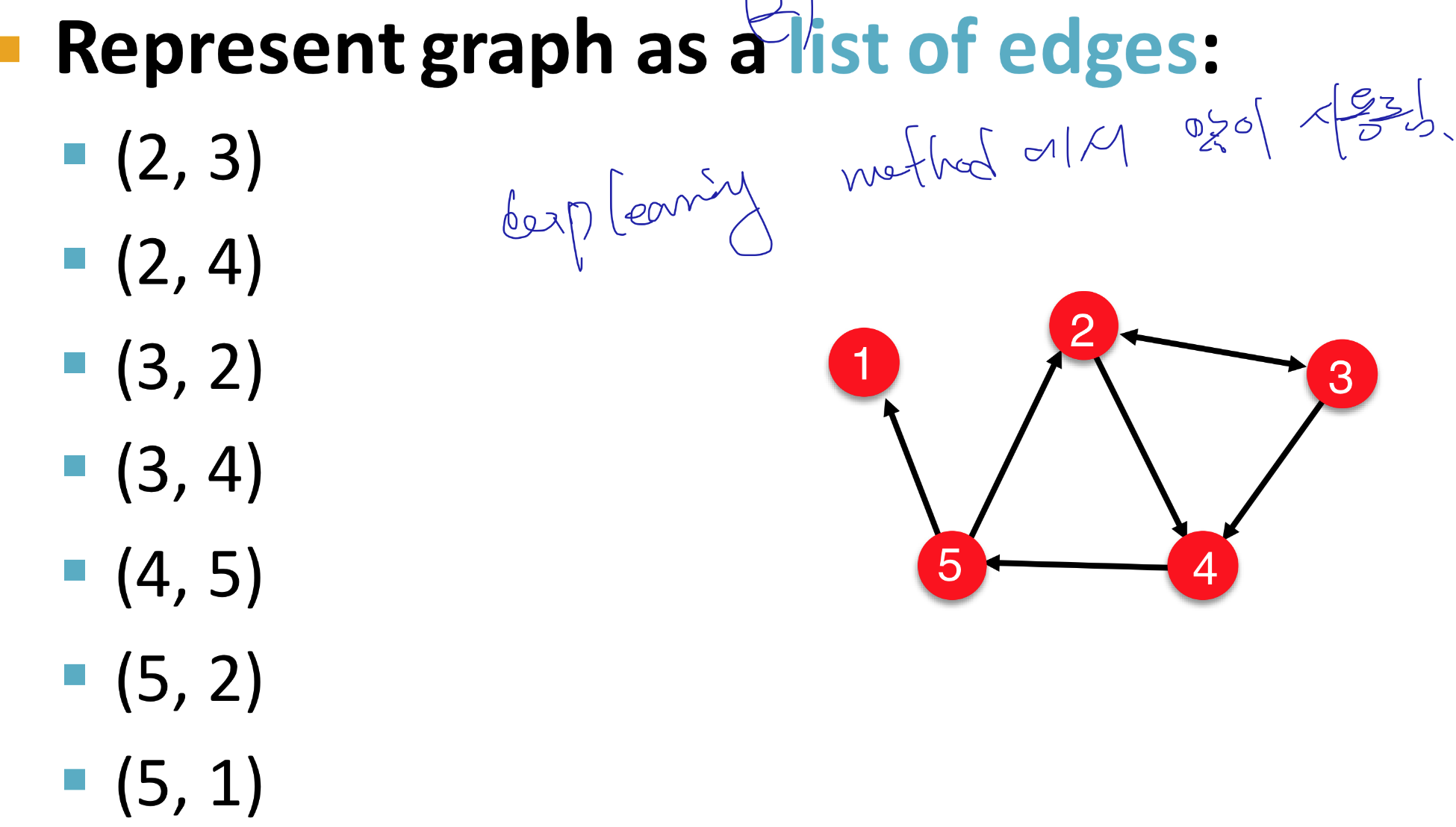
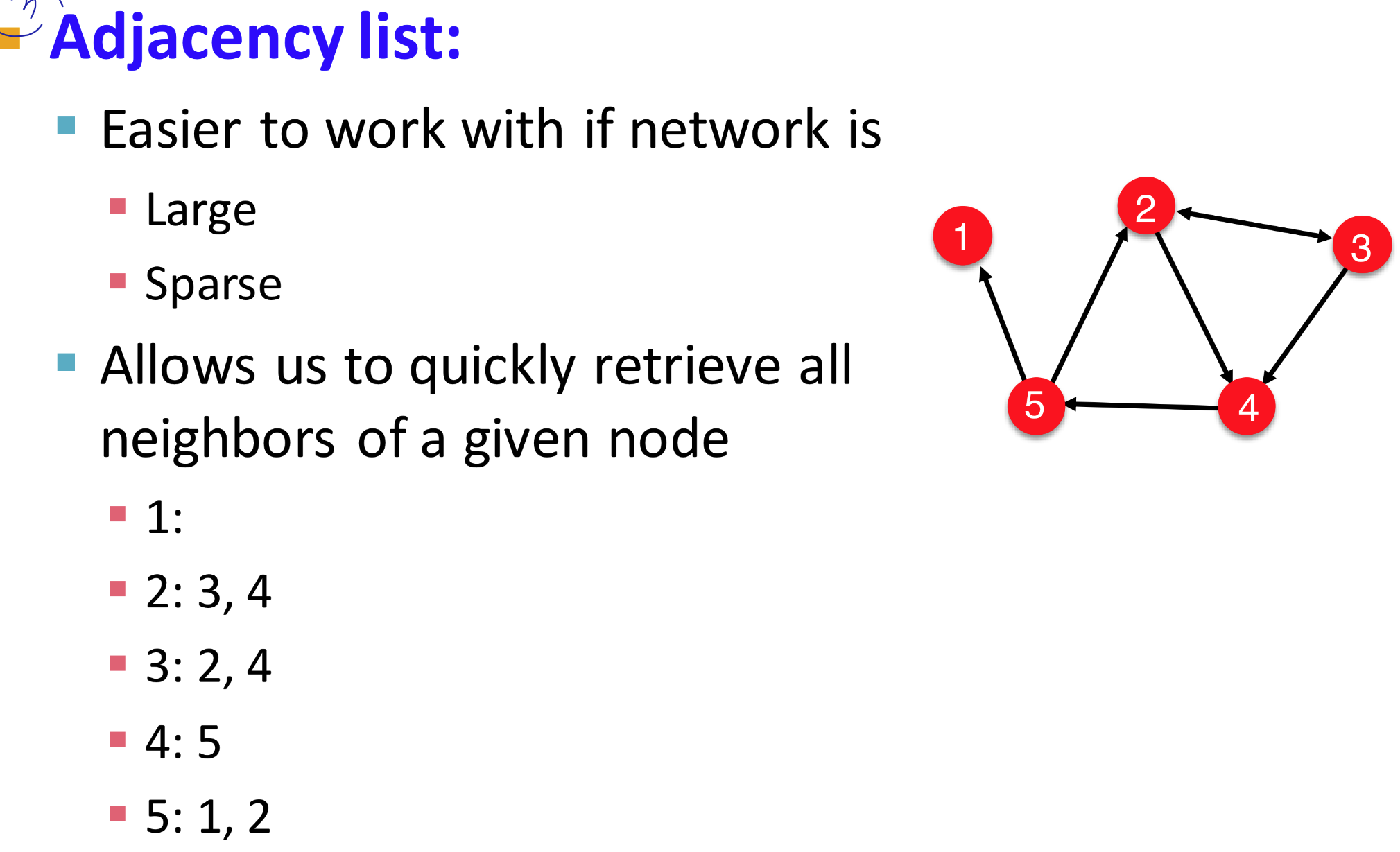
Adjacency list
Node and Edge Attributes
- 가중치(Weight) - 대화 빈도
- 등위(Ranking) - 절친, 친구
- 유형(Type) - 친구, 친척, 동료
- 부호(Sign) - 친구 vs. 적
- 나머지 그래프의 구조에서 확인 가능한 속성: 공통 친구의 수
More Types of Graphs
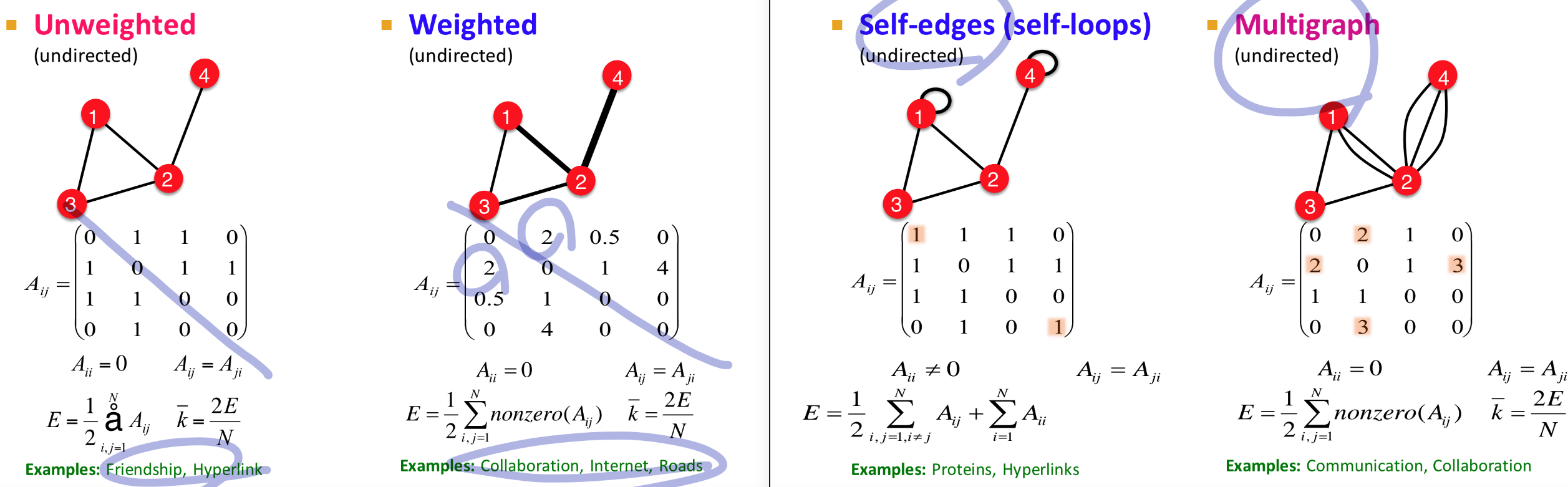
- Unweighted
- Weighted: adjacency matrix의 값이 0과 1로 나뉘지 않음
- Self-edges(self-loops): 자기 회귀형 노드가 있음
- Multigraph: 두 개의 노드간 다중으로 연결 가능
Connectivity of Undirected Graphs
disconnected 그래프는 두개 이상의 연결된 컴포넌트로 구성되어 있음
disconnected는 나머지 영역이 0으로 채워져 있음
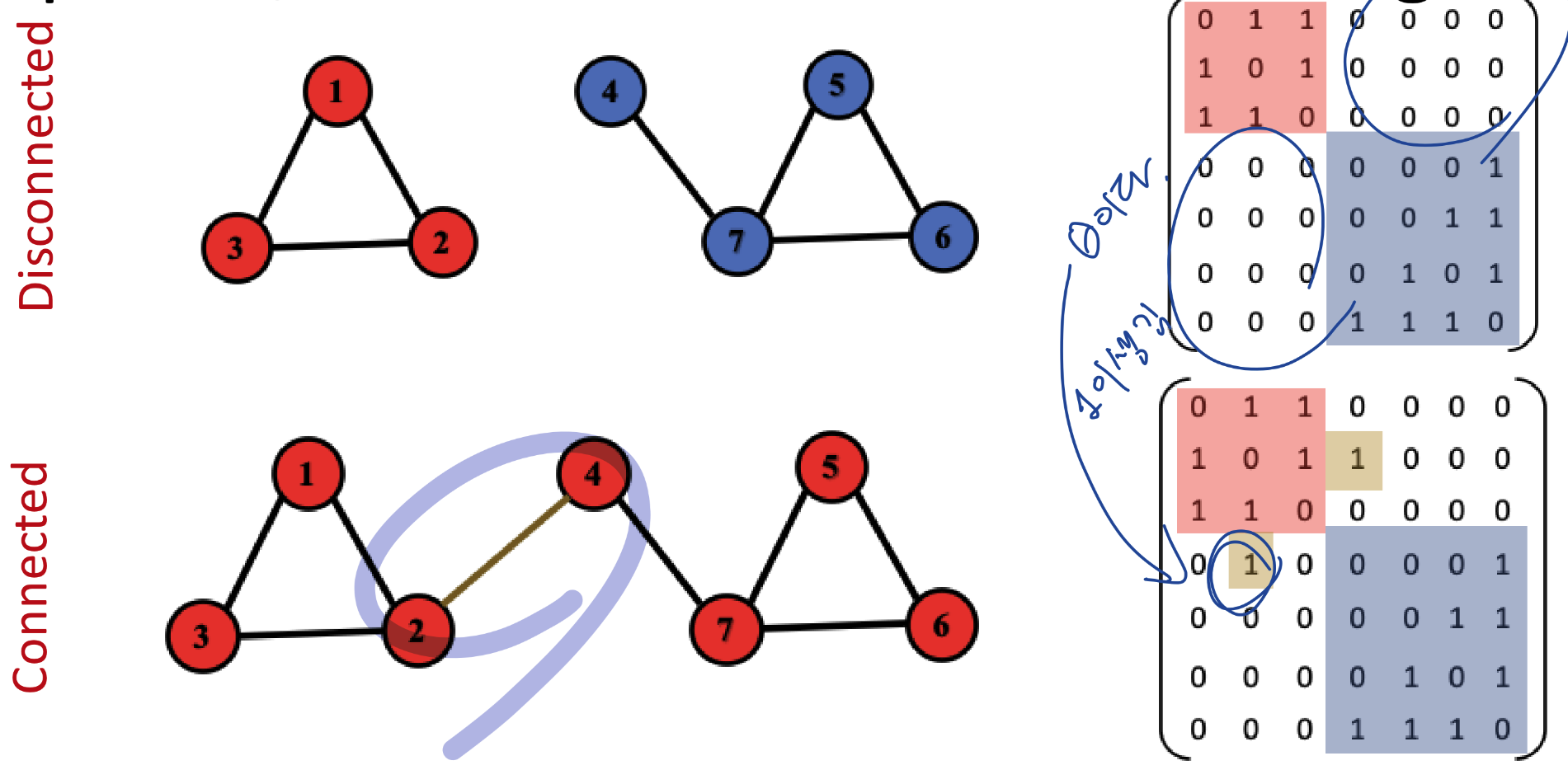
Connectivity of Directed Graphs
- Strongly connected directed graph: 모든 노드가 다른 노드로 연결된 path를 가지고 있음
- Weakly connected directed graph: 엣지의 방향성을 무시하면 연결된 것
Strongly connected components(SCCs): 컴포넌트 단위로 강하겨 연결된 것